Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
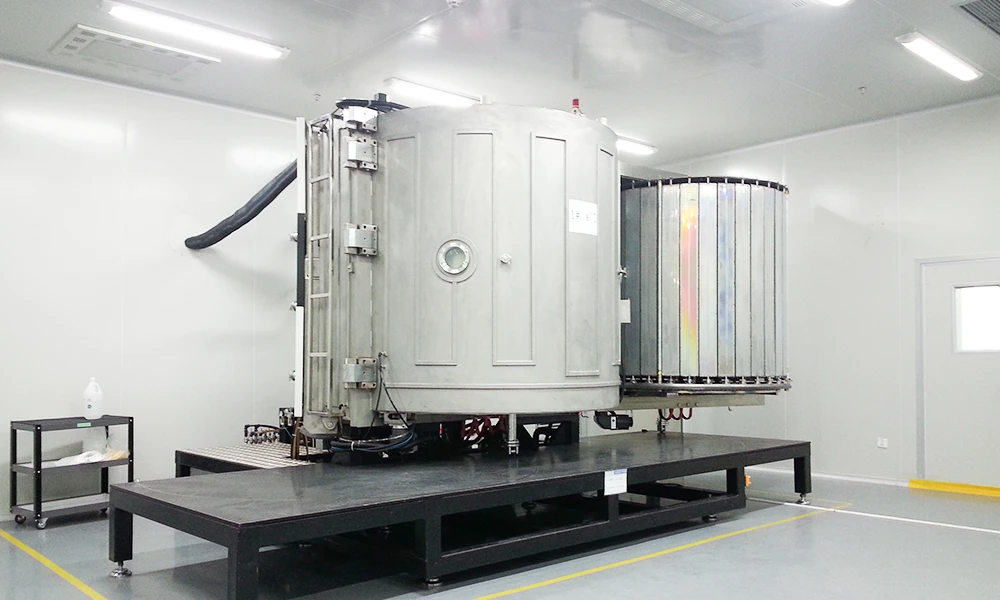

What's PVD?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a technology that, under vacuum conditions, uses physical methods to vaporize solid or liquid materials into gaseous atoms, molecules, or partially ionized ions. These are then deposited on the substrate surface through a low-pressure gas (or plasma) process to form a thin film with specific functions.
PVD technology can deposit not only metal films and alloy films but also compound films, ceramic films, semiconductor films, and polymer films. It is a relatively new surface treatment technology.
FirstMold utilizes PVD technology (through cooperative suppliers) primarily in the scenarios of plastic molds, die-casting molds, and CNC prototypes
Industry Applications

Wearable Technology

Mobile Communications

Metal Jewelry

Hardware Accessories
Automotive Components
Medical Device
Mold Industry

Watch Industry
Advantages of Anodizing for Your Product
High Hardness
Nickel coating: 180HV
Aluminum: 100HV
Anodizing: 300HV
Chrome plating: 800HV
PVD: 1600HV
Excellent Adhesion
PVDed parts can be bent over 90 degrees without cracking or peeling superior to other techniques like electroplating and spraying.
Aesthetic Appeal
Coatings come in a variety of colors, are evenly and uniformly colored, have a smooth and delicate surface, possess metallic luster, and never fade
Durable Surface
Scratch-resistant, difficult to scratch, does not peel or crack easily. Corrosion-resistant, acid-resistant, and oxidation-resistant.
Environmentally Friendly
Although the production process emits waste gases that require filtration, it essentially falls within the category of green manufacturing.
Physical Vapor Deposition Price
| PVD Process | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Ion Plating | Uses a high-energy ion beam to deposit material onto the substrate, often used for hard coatings. | $$ |
| E-beam Evaporation | Uses an electron beam to heat the material, which then vaporizes and deposits onto the substrate. | $$ |
| Ion Beam Assisted Deposition (IBAD) | Uses an ion beam to assist deposition, enhancing film adhesion and density. | $$ |
| Sputtering | Uses an ion beam to bombard the material, causing it to sputter and form a thin film on the substrate. | $ |
| Arc PVD | Uses arc discharge to form a dense film on the substrate, often for decorative and functional coatings. | $$$ |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Uses chemical reactions to deposit a film on the substrate, often for semiconductor and optical applications. | $$$ |
| Evaporation | Uses heating to vaporize the material, which then deposits onto the substrate forming a thin film. | $ |
| Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) | Uses plasma to enhance the chemical vapor deposition process, improving film quality. | $$$ |












